Scalable and Customizable Intent Inference and Motion Planning for Socially-Adept Autonomous Vehicles
Project Summary
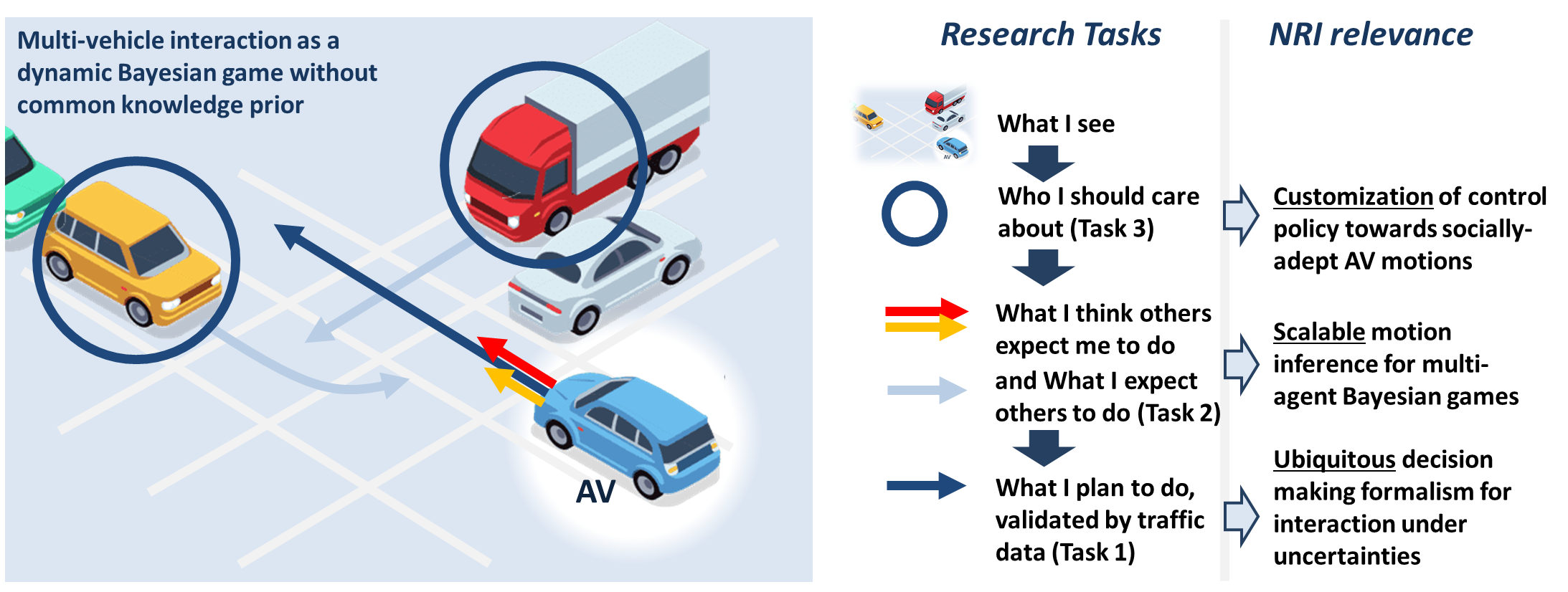
The overall objective of this project is to allow future autonomous vehicles to interact with multiple surrounding vehicles in a safe and socially-adept manner. This objective will be achieved by developing a novel algorithm framework for an autonomous vehicle to anticipate other vehicles’ behavior and customize its motion according to the local driving culture.
This project aims at answering two fundamental research questions: 1) what formalisms of intent inference and motion planning are capable of creating socially-adept motions, and 2) what embodiment of these formalisms can achieve scalability for multi-vehicle interactions and customizability for changing driving cultures?
To answer these questions, the research team will pursue the following three goals. First, the project team will build a Bayesian game model to represent vehicle interactions, and develop mechanistic intent inference and motion planning policies. Second, a message passing neural network will be developed to enable scalable intent inference and motion prediction of multiple surrounding vehicles. Third, a social attention mechanism will be developed that allows an autonomous vehicle to actively prioritize its various control considerations, e.g., safety and courtesy towards the surrounding vehicles.
Project Team
 Wenlong Zhang, PI
Wenlong Zhang, PI
 Yi Ren, co-PI
Yi Ren, co-PI
 Yezhou Yang, co-PI
Yezhou Yang, co-PI
 Sunny Amatya, researh assistant
Sunny Amatya, researh assistant
 Lei Zhang, researh assistant
Lei Zhang, researh assistant
 Varun Jammula, research assistant
Varun Jammula, research assistant
 Yi Chen, master’s student
Yi Chen, master’s student
 Tanner Merry, undergraduate (REU) student
Tanner Merry, undergraduate (REU) student
Project Alumni
Zachary Hoffman, 2019-2020
Undergrad Student (Computer Science), Arizona State University
Fulton Undergraduate Research Initiative (FURI), Spring 2020 and Fall 2020
Grace Zhang, Summer 2020
Undergrad Student (Computer Science), Stanford University
NSF REU Student
Publications
[J1] Y. Wang, Y. Ren, S. Elliott and W. Zhang, “Enabling Courteous Vehicle Interactions Through Game-Based and Dynamics-Aware Intent Inference,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles , vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 217-228, June 2020, doi: 10.1109/TIV.2019.2955897. Source code available here
[J2] K. Gunasekar, Q. Qiu and Y. Yang, “Low to High Dimensional Modality Hallucination Using Aggregated Fields of View,” in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1983-1990, April 2020, doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2970679. Source code available here
[C1] Y. Ren, S. Elliott, Y. Wang, Y. Yang and W. Zhang, “How Shall I Drive? Interaction Modeling and Motion Planning towards Empathetic and Socially-Graceful Driving,” 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) , 2019, pp. 4325-4331, doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2019.8793835. Source code available here
[C2] Y. Chen, L. Zhang, T. Merry, S. Amatya, W. Zhang and Y. Ren, “When Shall I Be Empathetic? The Utility of Empathetic Parameter Estimation in Multi-Agent Interactions,” 2021 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) , 2021, accepted.
Acknowledgement and Disclaimer
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1925403. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
